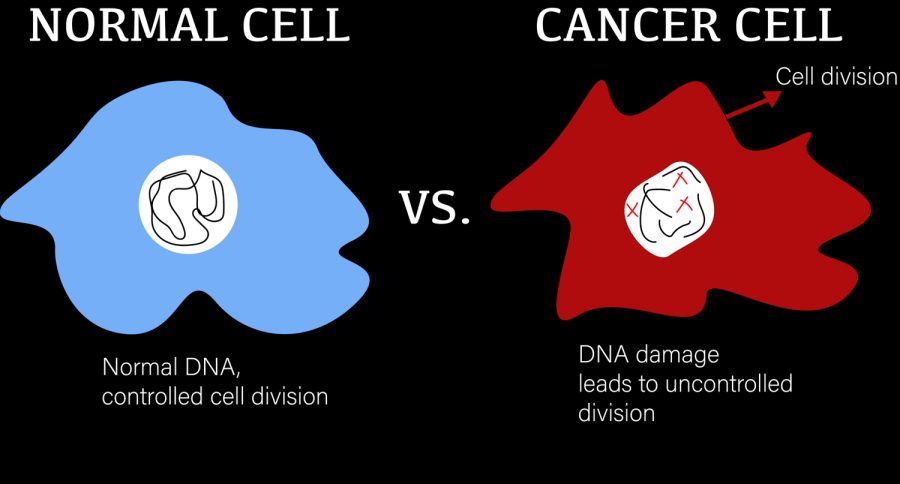
Science Explained: What causes cancer?
EMMA LEDBETTER and JOSIAH PIKE
• January 13, 2022
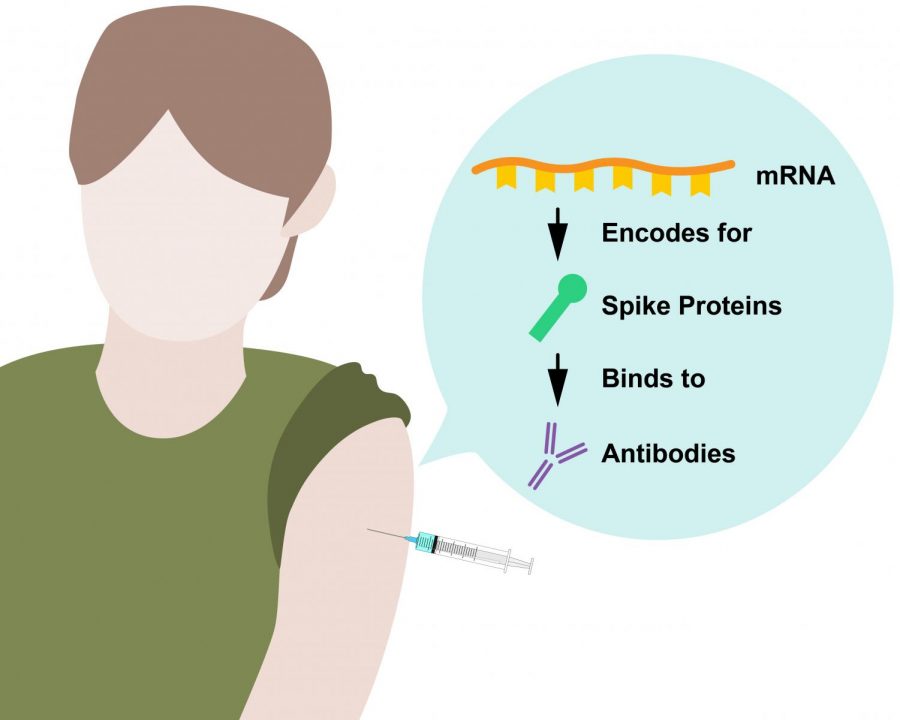
Science Explained: What does a booster shot do for immunity?
EMMA LEDBETTER and CALLIE GERBER
• November 18, 2021

Science Explained: Why is the Delta variant so contagious?
EMMA LEDBETTER, Evergreen news editor
• August 26, 2021
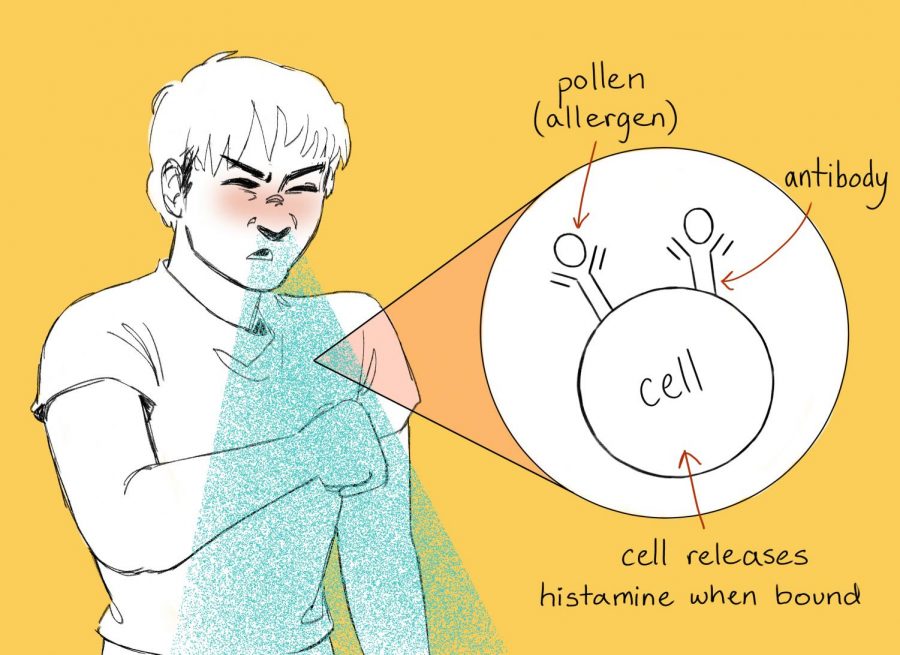
Science Explained: How do allergies work?
EMMA LEDBETTER, Evergreen news editor
• June 15, 2020

Science Explained: How do vaccines work?
EMMA LEDBETTER, Evergreen news editor
• June 10, 2020
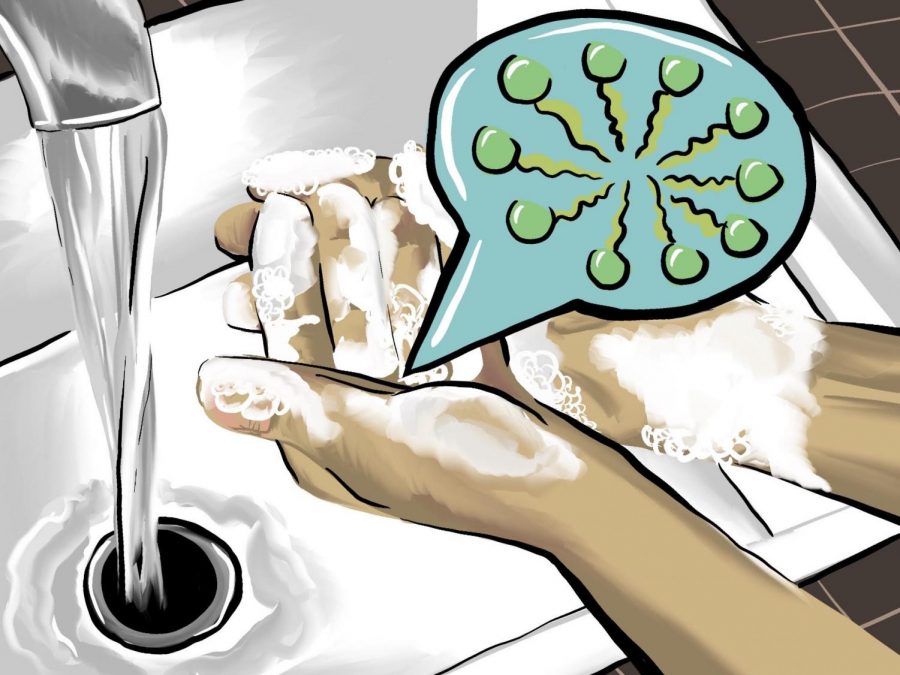

Science Explained: Why is hand washing more effective than using hand sanitizer?
EMMA LEDBETTER, Evergreen news editor
• May 27, 2020
Load More Stories









